Web and Social Network Analytics
Week 5: Ethics in Social Network Analytics
Feb-2026
Table of Contents
Welcome Back!
Last Week:
- Sentiment analysis for customer reviews
- Association rules and frequent itemsets
- Recommendation systems
This Week: Ethics in Analytics
- The responsibility that comes with data
- GDPR and privacy regulations
- Fairness in algorithmic systems
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to:
- Explain why ethics matters in web and social network analytics
- Identify key GDPR requirements for data collection
- Recognise sources of algorithmic bias in AI systems
- Apply Privacy by Design principles to ShopSocial
Privacy & Data Protection
Why Ethics Matters
The Stakes Are High
Every click, scroll, and purchase generates data. How we collect, store, and use this data has real consequences for individuals and society.
- Trust: Users who feel surveilled abandon platforms
- Reputation: Data breaches and misuse destroy brands
- Legal: GDPR fines can reach €20 million or 4% of global revenue
- Societal: Unchecked tracking enables manipulation and discrimination
Case Study: Cambridge Analytica (2018)
What happened:
- Facebook quiz app harvested data of 87 million users
- Used for political advertising without proper consent
- Influenced Brexit and US elections
Consequences:
- Facebook fined $5 billion (US)
- Cambridge Analytica dissolved
- GDPR enforcement accelerated
Lessons for ShopSocial:
- Consent must be explicit
- Third-party data sharing is risky
- Users expect transparency
- Build ethically from the start
📊 Quick Poll: Privacy Trade-offs
Wooclap Question
Go to wooclap.com and enter code: KMIAHE
What data would you share for a 10% discount on ShopSocial?
A. Purchase history only
B. Location data
C. Browsing behavior
D. None - privacy is more important
GDPR: Key Requirements
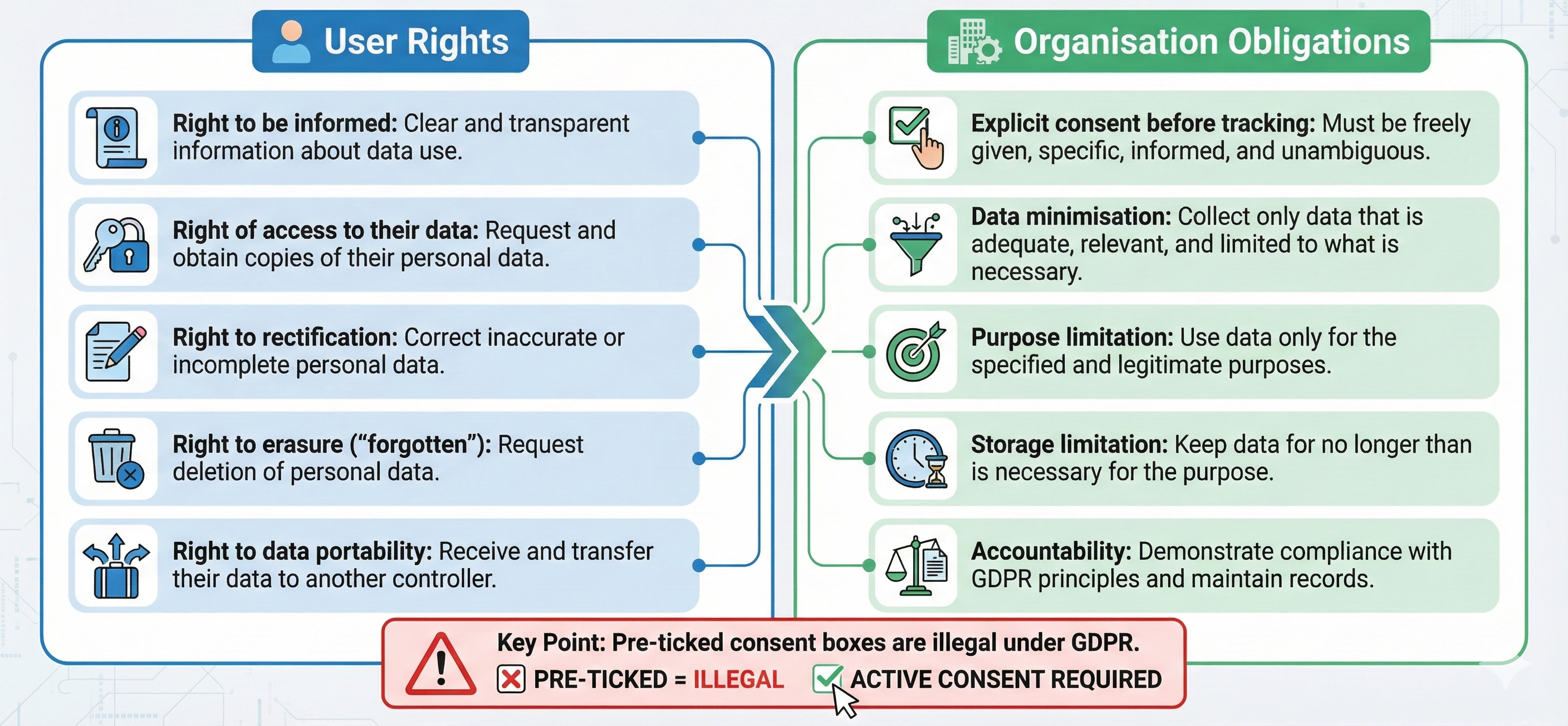
Privacy by Design: 7 Principles
- Proactive not reactive - prevent problems
- Privacy as default - most protective settings
- Privacy embedded - integral, not an add-on
- Full functionality - positive-sum approach
- End-to-end security - protect data lifecycle
- Visibility & transparency - open practices
- Respect for user privacy - user-centric
Applied to ShopSocial:
- Only track essential metrics
- Anonymise IP addresses
- Provide clear opt-out mechanisms
- Regular data deletion schedules
Fairness & AI Regulation
Fairness in AI: Real Cases
 Amazon’s AI Hiring Tool:
Amazon’s AI Hiring Tool:
Shut down after discovering gender bias - the system penalized female candidates.

ProPublica Investigation:
Recidivism risk scoring was biased against African Americans.
Algorithmic Bias: Sources
\[Data + Model = Prediction\]
Common Bias Sources:
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Selection Bias | Training data doesn’t represent population |
| Feedback Loops | Recommendations reinforce existing patterns |
| Omitted Variables | Missing attributes that affect outcomes |
| Societal Bias | Human biases embedded in historical data |
Key Insight: Simply ignoring sensitive attributes (gender, race) does NOT remove bias - it’s already embedded in other features.
🔍 Hands-On: Ethical Audit
Activity (3 minutes)
You’re auditing ShopSocial’s analytics. Assess each feature:
| Feature | Ethical Concern | Acceptable? |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized pricing | Price discrimination | |
| “Customers like you bought” | Filter bubble | |
| Abandoned cart emails | Manipulation | |
| Sharing data with advertisers | Privacy violation |
Discussion: Which features would you approve? What safeguards would you add?
EU AI Act: Risk-Based Regulation
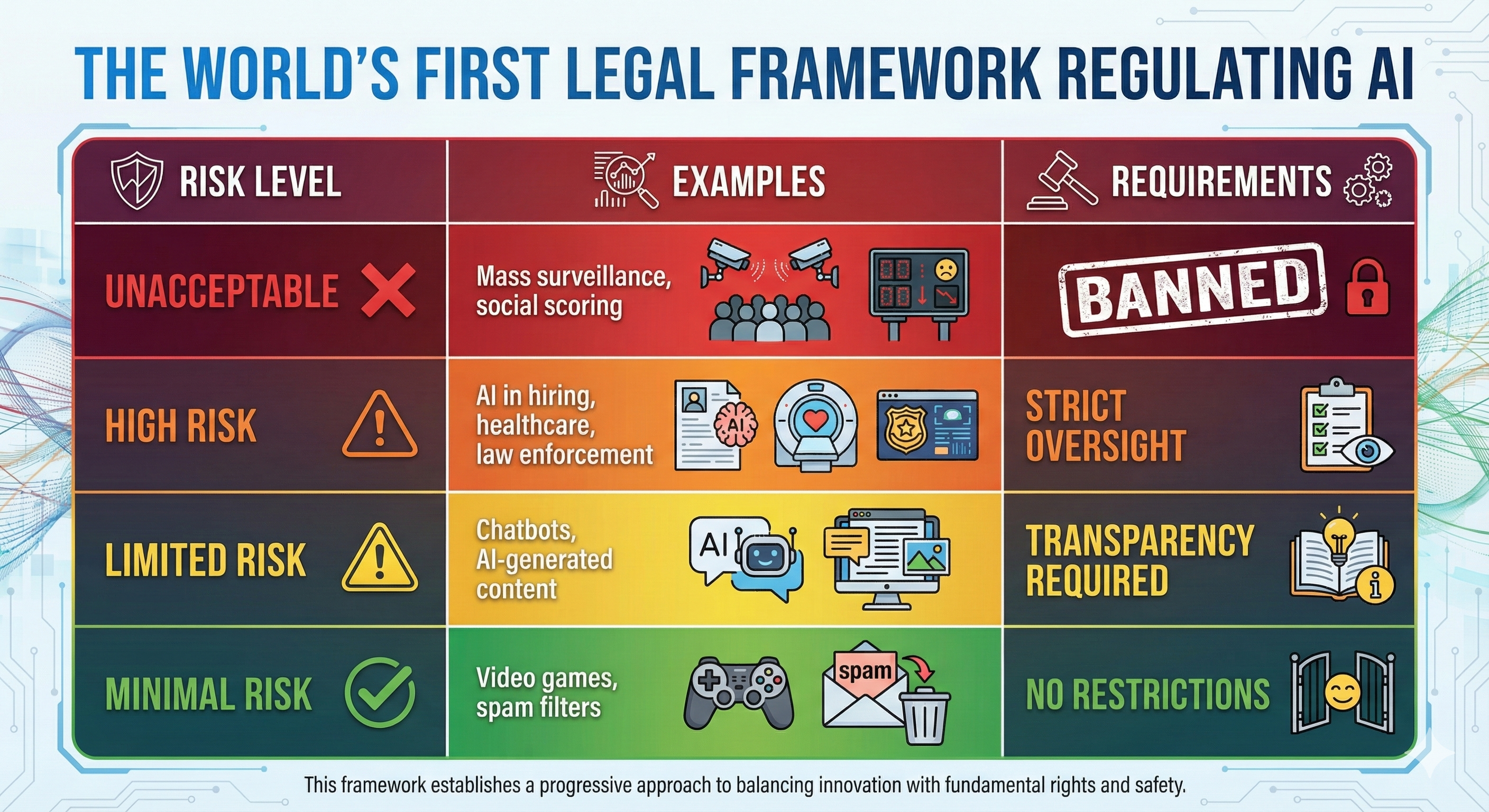
GDPR vs EU AI Act
| Aspect | GDPR | EU AI Act |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Personal data & privacy | AI systems & risks |
| Scope | Data collection/processing | AI model development |
| Key Concern | Consent & data rights | Fairness & safety |
For ShopSocial: Must comply with BOTH - protect customer data AND ensure fair AI recommendations.
Summary
Key Takeaways
Privacy:
- GDPR protects user rights
- Consent must be explicit
- Privacy by Design principles
Fairness:
- Bias enters through data AND algorithms
- Ignoring attributes doesn’t fix bias
Regulations:
- GDPR: data protection
- EU AI Act: AI risk classification
- Significant penalties for non-compliance
Practice:
- Ask: Do we need this data?
- Transparency builds trust
Course Wrap-Up
What You’ve Learned:
| Week | Topic |
|---|---|
| 1 | Web Analytics Fundamentals |
| 2 | Web Scraping & APIs |
| 3 | Social Network Analysis |
| 4 | Unsupervised Learning |
| 5 | Ethics & Regulations |
Next Steps:
- Apply these techniques to your ShopSocial coursework
- Consider ethics at every stage of your analysis
Questions?
Thank you!
Dr. Zexun Chen
Zexun.Chen@ed.ac.uk
Office Hours: By appointment
Good luck with your coursework!
